Endurance training is a powerful way to boost your energy and improve your cardiovascular health. Whether you’re just starting out or training for your first marathon, running reshapes your body from the inside out. This post will guide you through how endurance training improves your heart, lungs, and overall health in simple terms. Understanding these changes can inspire your journey and help you run stronger, feel healthier, and enjoy every step.

🫀 How Running Strengthens Your Heart and Fuels Energy
Your heart is the powerhouse of your running journey. When you train consistently, your heart learns to work smarter—not harder.
Marathon training gradually increases your heart’s stroke volume (how much blood it pumps per beat), meaning it doesn’t have to beat as often. This lowers your resting heart rate and protects your heart long-term.
Over time, your left ventricle—the heart’s strongest chamber—enlarges and becomes more efficient. It’s like upgrading from a compact car to a powerful engine. Even at rest, your body gets better at delivering oxygen-rich blood to every muscle.
This improvement isn’t just about athletic performance—it’s a sign that your cardiovascular system is adapting to the demands of movement.
A stronger heart means less strain on your body, faster recovery times, and a more stable energy output throughout your runs. You’ll feel less winded on hills, more relaxed on long distances, and more empowered overall.
Let’s take a closer look at how it works: the heart’s stroke volume increases, meaning the amount of blood ejected per beat goes from around 70–75 ml (in untrained individuals) to up to 120–150 ml in well-trained runners. That’s nearly double the delivery of oxygen and nutrients in the same time.

Heart Improvements
As a result, your heart doesn’t need to beat as frequently to meet the body’s demands. This is why runners often have resting heart rates 15–25% lower than average—sometimes as low as 40 beats per minute.
Even more impressive? Over time, this reduction in resting heart rate saves your heart up to 20,000 beats per day. It’s like giving your engine a longer life just by running.
Combined with improved cardiac output during exercise, these changes give your body a powerful and efficient circulatory engine to rely on for endurance and daily energy.
With continued endurance training, your body becomes more resilient to stress and illness, thanks to improved circulation and heart function. It’s one of the best long-term investments you can make in your health.
💬 “Your heart is more than a muscle—it’s your resilience in motion.”
🌬️ Breathe Deeper, Run Stronger – Lung Benefits of Endurance Training
At first, you may feel out of breath. But with regular endurance training, your lungs grow more efficient. You begin breathing deeper, slower, and with more control.
The breathing muscles—like your diaphragm—grow stronger, and your lung tissue becomes more elastic and flexible.
The real magic happens in the alveoli, the tiny air sacs at the ends of your lungs. With time, more alveoli open up to exchange oxygen for carbon dioxide, allowing you to absorb more oxygen with each breath. This means more fuel to your muscles and better performance.
When you’re at rest, you typically take 10–15 breaths per minute, inhaling around 500 ml of air per breath. That’s only about 6 to 7 liters of air moving through your lungs every minute.
But during a run, your breathing rate can climb to 40–60 breaths per minute, and each breath may pull in 2 to 3 liters of air.
That’s over 100 liters of air circulating per minute, dramatically increasing your oxygen intake. It’s like going from sipping through a straw to opening a wind tunnel.
Over time, your lung tissue becomes more pliable, and your breathing pattern becomes more economical.
The muscles that support your breathing—especially the diaphragm and intercostal muscles—strengthen through this repetitive motion, allowing you to breathe more efficiently even during intense exertion.

Endurance training – Improvements
As your endurance builds, your breathing becomes rhythmic and instinctive. This not only supports oxygen delivery, but it calms your nervous system.
Many runners report a meditative state during longer sessions—a peaceful rhythm of breath and movement. That’s your lung capacity and control working in harmony.
You may not notice these internal improvements day to day, but when you’re able to speak in full sentences during a long run or run up a hill without gasping, that’s your respiratory system doing its job. You’ve trained your lungs to meet the moment.
Over months of consistent training, your pulmonary system strengthens enough to support efforts you once thought impossible.
Tasks like climbing stairs or running a mile without stopping become easy, not because you’ve changed who you are, but because you’ve trained how you breathe.
🔁 How Blood Adaptations Power Your Muscles and Mind
Think of your circulatory system as a vast highway network. With endurance training, traffic becomes faster and smoother.
Your blood volume increases, your blood vessels expand, and more capillaries form around your working muscles.
These capillaries are the tiniest of blood vessels, and they serve as bridges between your arteries and your cells.
As the number of capillaries increases—what we call capillarization—oxygen can be delivered to your muscles more efficiently.
This is a huge benefit for runners, because it means that your legs receive oxygen faster, use it more effectively, and fatigue more slowly.
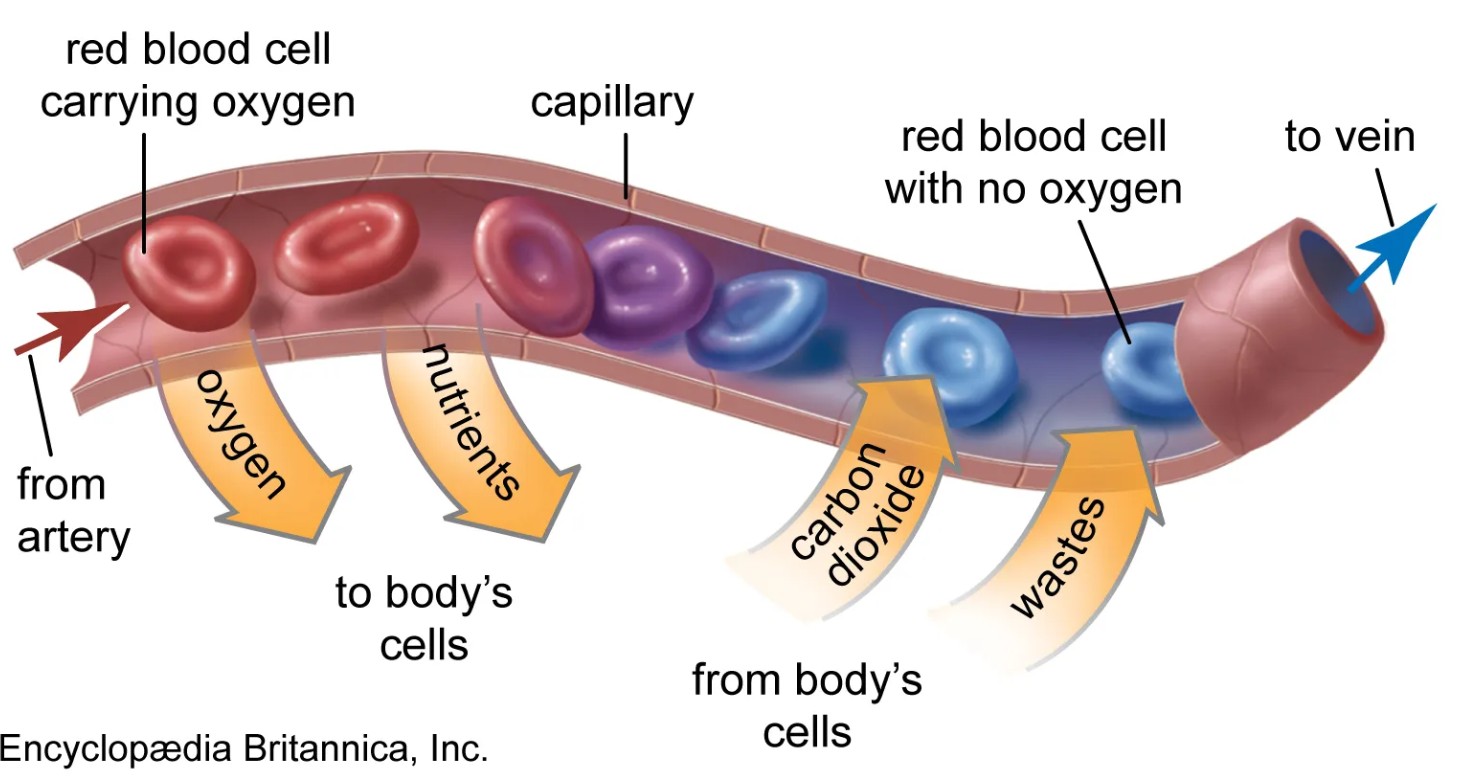
This means oxygen gets delivered more efficiently to the tissues that need it most. Your muscles also become better at using that oxygen thanks to increased mitochondria—the power plants of your cells.
Mitochondria multiply in response to training and are able to use the delivered oxygen to create more energy in the form of ATP, your body’s basic fuel.
There’s also an increase in the total blood volume itself—up to 20–25% higher than in untrained individuals.
More blood volume means more fluid to carry nutrients, oxygen, and waste, improving thermoregulation and reducing cardiovascular strain.
The result? Your muscles fatigue less quickly, your stride feels lighter, and your recovery speeds up. You may even notice your fingers and toes staying warmer in colder weather, or that your post-run fatigue fades quicker than before.
The circulatory system doesn’t just support performance—it supports health. With improved blood flow, you reduce the risk of blood pressure issues, blood sugar imbalances, and even chronic inflammation. And with more consistent training, your cardiovascular age may even become younger than your biological age.
💬 “Stronger circulation doesn’t just power your legs—it powers your life.”
🩸 Blood Adaptations – More Oxygen, Less Stress
Your blood is a hero in this story. As you train, your body produces more red blood cells and hemoglobin—the proteins that carry oxygen.
This means your working muscles get more oxygen, faster. The hematocrit value—the percentage of red blood cells in your blood—also rises.
This leads to stronger performance and endurance. A higher hematocrit value means more oxygen-rich blood is circulating with every heartbeat.
In men, a typical hematocrit value ranges between 40–45%, while in women it’s slightly lower—between 38–43%. As you train regularly, these values may rise slightly, increasing your body’s capacity to transport oxygen.
This gives your muscles more fuel and improves your overall endurance. That’s why you’ll often hear people talk about the blood as the ultimate “delivery service”—bringing nutrients and oxygen to where they’re needed and clearing waste efficiently.
Over time, running also lowers harmful LDL cholesterol while improving HDL, the good kind. Your blood becomes more efficient at regulating heat, too, helping you stay cooler during long summer runs.
There’s even evidence that endurance training improves your blood’s ability to buffer lactic acid, meaning you feel less burn and fatigue during hard sessions.
What’s even more powerful is that these adaptations happen quietly. You won’t always feel them, but you’ll notice when your runs become smoother, your breathing less labored, and your strength more consistent. These are signs your blood is working better for you.
Additionally, improved blood regulation means more waste products like CO2 and lactic acid are cleared faster.
You recover sooner, and you’re less likely to feel dizzy or nauseated after longer efforts. It’s a subtle but crucial part of the endurance process.
🔥 From Chaos to Calm – How Endurance Training Balances Your Body

With consistent training, your body learns to redirect blood flow to where it’s needed most. During a run, blood shifts from digestion to muscles or to the skin for cooling.
This is controlled by your autonomic nervous system and fine-tuned over weeks and months of training. Your temperature regulation improves, making you more resilient in heat and more adaptable to cold.
This means fewer chills, less overheating, and a more stable performance across seasons.
It’s also common to notice that once cold fingers or stiff knees become warmer and more flexible. That’s better blood flow at work.
As the body becomes more skilled at regulating itself during movement, you also lose less sodium in sweat, and your hydration system becomes more efficient.
You’ll notice you cramp less, recover faster, and feel more in tune with your own needs while running.
These subtle changes build over time, helping you feel stronger, more capable, and less fatigued after workouts. But the effects go deeper than muscle tissue.
Internal regulation impacts how your nervous system reacts to stress. As your body learns to balance blood flow and oxygen delivery, you may experience improved sleep, better digestion, and more even mood regulation. These are the unsung victories of endurance training.
Many runners describe a new sense of inner calm after several months of training. Feeling balanced, grounded, and physically prepared for daily life is often the biggest reward—not a medal, but a sense of control over your energy and strength.
💬 “Feeling balanced isn’t a bonus—it’s the goal of every mile.”
❓ FAQ – Endurance Training for Beginners
What’s the best way to start endurance training? Start slow with run-walk intervals, and increase mileage gradually. Aim for consistency, not speed.
Can I do endurance training if I’m over 50? Absolutely. Many runners begin later in life and thrive with steady aerobic training.
How long before I notice changes? Most people see heart rate and breathing improvements within 4–8 weeks of consistent training.
Does endurance training burn fat? Yes. As your aerobic system improves, your body becomes better at using fat as fuel.
🎓 Final Thoughts
Endurance training is a quiet revolution inside your body. You may not see the changes right away—but your heart beats stronger, your lungs stretch deeper, and your blood runs more efficiently.
It’s a transformation that builds confidence, stamina, and lifelong health. And the best part? It all starts with a single run.
💬 “Each step forward isn’t just training your legs—it’s strengthening your life from the inside out.”
📣 If you found this helpful, share the post with your fellow runners. Let’s build healthier hearts together.






This is an excellent article, full of essential information for any endurance athlete, who trains and competes at any level. It is essential to understand what happens within your body and the changes that take place so that it can adapt and work for endurance. I recommend anyone interested in endurance reads this. Knowledge is power.
Hi Castle
Thank you for your comment. Happy that you can use some of it.
Be Well