How your body processes and uses oxygen during a distance race and in the initial stages of intensity training may not seem very exciting. But the most crucial in Marathon training is the body’s Oxygen system. Newer research suggests that understanding this process and adjusting your pre-race preparation can provide significantly better performance in the race.
The Oxygen System (respiratory system) is about the aerobic processes. As a runner, Oxygen uptake varies from person to person. Most crucial in Marathon training is the Oxygen system, which depends on a person’s ability to:
- Take up oxygen
- Transport of Oxygen
- Release Oxygen to the energy-consuming tissues
- Consume Oxygen
Cardio Vascular Circulatory System And Oxygen
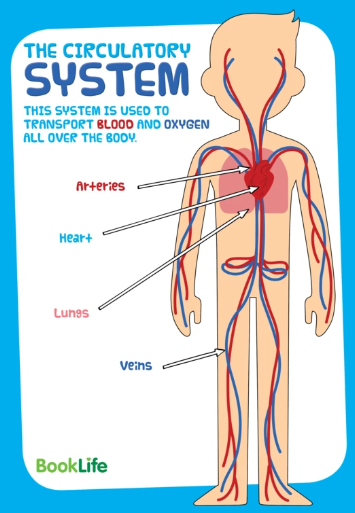
It is the cardiovascular system, which provides Oxygen transport. When you have inhaled air into the lungs, Oxygen goes from the air through the lungs alveolar wall and the capillary wall into the blood, which flows in the thin blood vessels around the lung alveolar.
The Oxygen in the blood binds to a protein molecule, hemoglobin, within the red blood cells.
The blood pumps around in the body of the heart and via the blood vessels; the blood comes to the muscles. Finally, the oxygen is absorbed into the muscle fibers, where the major part consumes by the working muscle fibers associated with ATP production.
The concentration of oxygen in the blood remains relatively constant. There are primarily three opportunities to influence the amount of oxygen, which carries out to the muscles and consumes there:
Shorter Distance For The Oxygen From The Blood And Into The Muscle Fiber
This happens mainly with more capillaries around each muscle fiber, and that the muscle fiber is not too thick, as it gives a longer distance into the muscle cell. It is therefore not an advantage to have big muscles if you want to achieve good results in long-distance races.
More Blood To The Muscles Per Time Unit Brings More Oxygen
More blood to the muscle per. time unit can only be affected in two ways. If the heart pumps more blood overall, or by more of the blood that the heart pumps, goes to the working muscle. Thus, the heart’s pumping ability becomes essential for the blood supply to the active muscle.
The pump capacity is measured in liters/minute. This minute volume will depend on, how many times the heart pulls together per minute, and how much blood the heart pumps out per contraction (stroke volume).
This gives:
Minute volume = heart rate * Stroke volume
The heart rate increases with the intensity of work, from a baseline value at rest, up to a maximum value at very high work intensity. The heart rate changes gradually and the work intensity must be maintained for a reasonable period before the heart rate is set at a stable level.
Increased Consumption of Oxygen in the Muscle Fiber
Besides increasing the supply of oxygen to the muscles, it is also important to increase the muscle’s ability to consume the amount of Oxygen. A muscle’s ability to consume Oxygen becomes better if the biochemical processes that consume Oxygen in the muscle increase.
These processes take place largely in mitochondria also called” power stations” and controls by specific enzymes. As training increases, the quantity of the specific enzymes and the size of mitochondria can increase up to 35 %.
All three factors above are influenced very positively by marathon training.

Oxygen Test – A Measure Of Progress
A way to detect the running progress is to measure your Oxygen uptake e.g. today and then again after a period of a few weeks or months. It is common to use the maximum Oxygen uptake as a reference target for performance ability.
Most of us have heard about the concept of fitness rating. This ‘number’ is a measure of how many milliliters of oxygen a person can uptake (absorb) per minute per kg. body weight. It uses as a measure of the maximum Oxygen uptake ability.
The most exact measurement of the maximum Oxygen uptake takes place in a laboratory with a Gaz analyzing machine that measures the volume of oxygen, where you wear a mask connected to a stationary metabolic system, this ensures that all breathing is through the mask.
The air you exhale while running on the treadmill collects. The maximum Oxygen uptake calculates by measuring the difference between the amount of Oxygen in the exhalation air and the amount of oxygen in the inhaled air plus taking blood samples to measure the lactate levels and other parameters during the test period.

The Oxygen uptake ability uses to express, how well your fitness is. The size of the maximum oxygen uptake (VO2 max.) concerning a person’s weight expresses as a number called fitness rating.
When a person for example has a fitness rating of 55, it means that he is able to absorb 55 milliliters of Oxygen per. Kg. body weight per minute. The fitness rating or the maximum Oxygen uptake is therefore an expression of the body’s current maximum aerobic capacity. This capacity has great importance for your performance in long-distance races.
Oxygen Uptake – Fitness Rating
Now, not all of us have the opportunity to be tested periodically with special equipment in a laboratory. However, there are other practical ways; you can use to test your progress. Find a flat test route e.g. in your neighborhood that takes 20 to 40 minutes to run. Run this route in the shortest possible time. Next, run this route periodically with 1 – 2 months intervals, and thus follow your progress by comparing your distance times.
If you want a pronounced fitness rate, you can use the classic Coopers 12 minute running test. This Test is also used with success when recruiting personnel to the military. In the test, you have to run as long as possible in 12 minutes.
Cooper 12 Minute Run Test – A Practical Fitness Test
The test performs on a flat section – preferably a real 400 m tracks on a stadium. The test requires that you can push yourself and that you may dispose of your run. Distance is fairly independent of age, sex, and body weight and therefore a good target for your fitness.

Here is how you do it:
1. Warm-up with about 15 – 20 minutes easy run followed by
stretching.
2. Run for 12 minutes as long as you can.
3. Measure up the distance covered.
4. Find your fitness rate with your covered distance in the table below:
| Running distance in meters | Fitness rating/ Man | Fitness rating/ Woman |
| 1500 | 22 | 23 |
| 1600 | 24 | 26 |
| 1700 | 27 | 28 |
| 1800 | 29 | 30 |
| 1900 | 31 | 33 |
| 2000 | 33 | 35 |
| 2100 | 36 | 37 |
| 2200 | 38 | 40 |
| 2300 | 40 | 42 |
| 2400 | 42 | 44 |
| 2500 | 45 | 47 |
| 2600 | 47 | 49 |
| 2700 | 49 | 52 |
| 2800 | 51 | 54 |
| 2900 | 54 | 56 |
| 3000 | 56 | 59 |
| 3100 | 58 | 61 |
| 3200 | 60 | 63 |
| 3300 | 62 | 66 |
| 3400 | 65 | 68 |
| 3500 | 67 | 70 |
| 3600 | 69 | 73 |
Fitness Ratings And Calculation
The maximum oxygen uptake or fitness rating of the untrained person is usually between 30 and 40 ml of oxygen per minute per kg. This Fitness rating test is not 100% valid, since there can be differences in Oxygen Utilization Rate, but that only makes sense when you are very experienced as Runner.
Joggers are between 45 and 60 ml of oxygen per minute per kg. Elite runners have a fitness rating of more than 80 ml of oxygen per minute per kg. If you want to estimate the VO2 max. by a calculation, you can insert the running distance in this formula:
VO2 Max. = (Distance covered in Meter – 504, 9)/ (44, 73)
If you are interested in Oxygen and its influence on your performance like me, I hope you like this page and if you have any questions about the topic or want to leave your own Personal review, please leave a comment below.






Thank you for explaining how the oxygen is used in the body when you put it under a lot of stress such as in distance running. How would you find some place to measure the amount of oxygen you use when training for a marathon? Is it correct to assume the the better you utilize the oxygen in your body, the faster you can run?
Hi Carolyn
Thank you for your comment. I really appreciate it.
In practice you can find a route on 3 – 5 km – use ex. a gps. Start running it as fast as you can. Note the time. Then run the same route again in about 1 -2 months later – following your running program. If you have been faster than last time you have increased the Oxygen level. A blood test would be precise, but that is not necessary.
Yes it’s true the better you utilize the oxygen in your body, the faster you can run. That is why the Oxygen system is so crucial in running.
– Sorry for the late answer
Be Well
Hi there this is really a nice niece of review it was really helpful. In whatever task or work we do we need oxygen. Oxygen is the basis of our existence. When we run we use up a lot of energy so we need to constantly refill those energy by taking a lot of energy. In the early hours of the morning I usually run up to about 8-9minutes as a way of boosting my stamina.
Hi Philebur
Thank you for your comment. Happy that you find it helpful.
You got it
Great habit you have there
Be Well
helloo dear, thanks alot for sharing such an amazing content, seeing your post has really giving me the mind of writing some helpful related post like yours, i learnt alot, your article is really of great and nice rating, i already saved these post so as to come back for future referencing, ireally love your work here, ill surely do some recommendation
Hi Skuchmane
Thank you for your comment. Happy that you could learn from it and want to do some recommendation.
– Sorry for the late answer
Be Well