Few people want to do something just because it’s healthy. It should also be fun and nice. You simply become a new and better person after a good run. When reading how to easily understand why running is important, we will explore that. But wouldn’t it be particularly beneficial to understand the Body’s ‘Main engine’? Heart circulatory system is the body’s engine. Learn once and for all why running has a huge positive impact on it.
Running is associated with strong feelings about life and death, escaping persecution, or just a simple play in childhood. When we run, we come in contact with the body’s memories. The benefits of running are many.
Running Strengthens the Heart’s Circulatory System

Many physical gains can be achieved through running training but the three most important that work as a coherent whole are Heart and lung functions that can undergo a huge improvement by running.
Breathing and oxygen transport during running
The function of the lungs is to supply the body with oxygen. When you are sedentary in rest, about 5 liters of air is drawn in and out per minute. This amount can increase during running to 200 liters.
The respiratory muscles become stronger during running training, but the lungs do not change size, even as the shape improves. In practice, humans are endowed with oversized lungs.
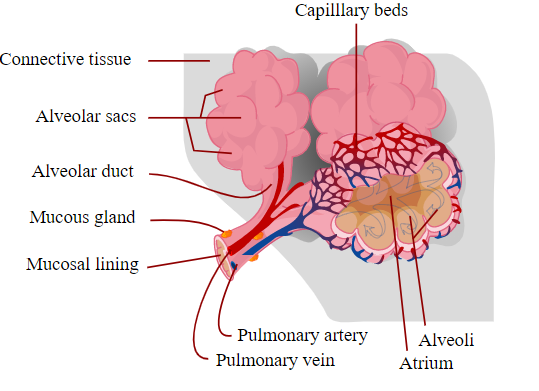
The air is drawn in through the mouth or nose, continuing down through the trachea, where it is distributed into the bronchioles. From here it is carried out into small air spaces, called alveolar, where the exchange of oxygen and CO2 takes place.
Each alveolar is surrounded by a network of thin blood vessels and the distance between blood and oxygen is so small that the exchange can occur extremely quickly. Inhalation takes place using the muscles between the ribs and the large muscle in the diaphragm.
When the muscles contract, the chest is raised too and the lungs follow along. This causes a negative pressure in the lungs and air is drawn in to equalize the pressure. Exhalation happens when the muscles relax, which creates overpressure, and the air is pressed out again.
By strong exhalation, the abdominal muscles can be activated. In this way, the muscle in the diaphragm is pressed further up into the chest. Exhalation can be further increased by other muscles, which compresses as well, so the lung volume becomes even smaller, which leads to a further enhanced exhalation.
Running and Pulmonary Ventilation
The amount of air a person exhales per minute is called pulmonary ventilation, it has two variables – the depth of respiration and the frequency of respiration. The depth of respiration is the amount of air that can be drawn in with each breath. It varies from ½ liters per minute at rest to 3 -5 liters during hard work, when we e.g. perform interval training in running.
The frequency of respiration, i.e. The number of breaths per minute, is the second variable. It is 10 – 12 at rest but can increase up to 40 – 50 at hard physical exertion. The total pulmonary ventilation can thus be expressed as the respiratory rate x the depth of respiration.
Heart And Circulatory System vs Oxygen Uptake
At rest, the body requires about 250 ml of oxygen per minute to keep going. Under maximum physical load, such as during a marathon, the need for oxygen can be increased by a factor of 20. It is rarely a problem to get enough air because even under maximum load we only utilize 2/3 of the total lung capacity.
On the other hand, the oxygen uptake, i.e. The ability of the blood to absorb and deliver oxygen, as well as the heart’s pumping ability are limiting factors for physical performance.
Oxygen Transport
Once the oxygen is transported into the blood, it binds to the dye hemoglobin of the red blood cells. The blood is then pumped around in the body and the oxygen is absorbed by the cells that use the oxygen in the energy supply.
Poor fitness does not mean an inability to draw air into the lungs, which are actually ‘oversized’ in this regard. But the bottleneck is to get enough oxygen transferred from the alveolar to the blood and further into the muscle cells.
Heart Circulatory System
The heart is the body’s most enduring muscle. It is made up of branched muscle cells in a fine and dense network, which is supplied with blood from the coronary artery system. It’s an internal system that only supplies oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle.
If this supply works optimally, the heart contracts evenly and rhythmically about 100,000 times a day.
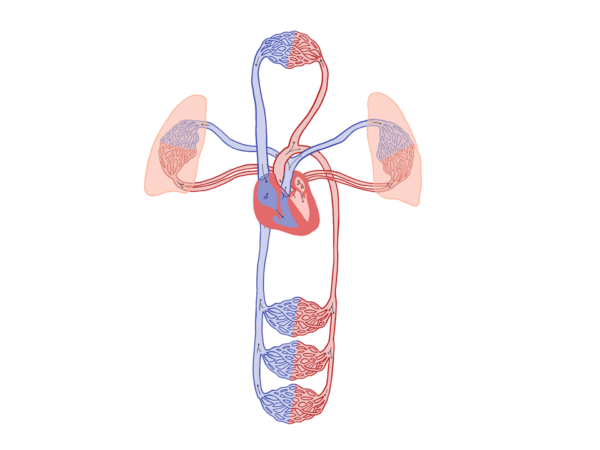
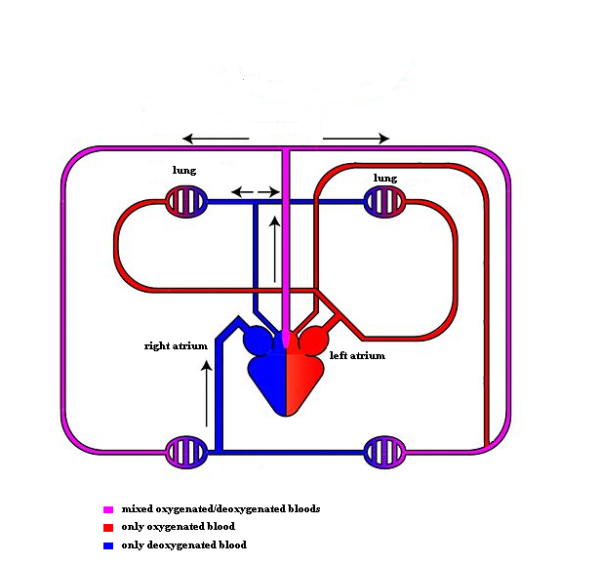
The heart valves ensure that the blood only can flow in one direction. When the heart rhythm is divided into three parts, it is due to a system of pumping phases, where the blood is sent through the four chambers and out to two different circulation systems.
The small circulatory system
The ‘used’ oxygen-poor blood is pumped from the right heart part to the lungs, where it is oxygenated and releases carbon dioxide for exhalation.
The big circulatory system
The oxygenated blood from the pulmonary circulation is sent via the left heart part to the muscles and organs in the body. The left side of the heart must perform a much larger pumping work and is therefore much thicker and stronger than the right side of the heart.
The pumping capacity of the heart
The pumping ability of the heart is crucial for the blood supply to the working muscles. The capacity here is measured in liters of blood per minute, which is called the minute volume.
The minute volume is conditioned by how many times the heart contracts per minute and how much blood the heart pumps out per beat. This number is called stroke volume. The formula for the work of the heart therefore becomes:
Minute volume = number of heartbeats per minute x stroke volume.
Circulatory System Functions Improves By Running

Running strengthens both the respiratory muscles, the heart, and the cardiovascular system. In general, you will be able to feel deeper and slower breathing as you get in better shape and when you have been running for a longer period, your lung tissue will become more flexible and elastic. Other greater effects and benefits are:
- The heart muscle is strengthened by running training and the efficiency of the heartbeat is increased, so more blood enters the system with a lower number of heartbeats
- More oxygen and power potential. The number of alveolar in the lung tips increases, which means that more oxygen can be delivered to the blood. Several capillaries are formed around each muscle cell, so the way for oxygen from the blood into the muscle cell becomes shorter.
- Your fitness rating increases. The average fitness rating is about 35 – 45 when you are 30 – 40 years. Trained runners often have a fitness rating of 55-60 while top athletes can be at 80-85 or more.
- The utilization rate is increasing. The muscles’ ability to absorb and consume oxygen is improved. The resting heart rate drops by 10 – 20 beats per minute when you have trained for 3 – 4 months. This means that your physical capacity increases.
- Since training works specifically, the muscle groups are strengthened differently. When you run, it is therefore, especially the oxygen absorption capacity in the leg muscles that will develop.
The effects of running?
Other gains that will enhance your life quality and surplus by running are:
- Reducing the risk of developing diabetes.
- It strengthens bones, muscles, and joints.
- Providing energy and surplus in everyday life
- Your brain sharpens
- You will sleep better
- Running makes you happier in many ways
- The immune system strengthens
Based on an assessment of effectiveness about costs, running will take a convincing first place when it comes to Cardiovascular effects. It is only cross-country skiing, which can do it better but it requires more costs such as snow and ski equipment.
Final Thoughts
Remember human physiology doesn’t change overnight as a ‘high-tech product’. It has taken hundreds of years to develop our physiology. So, you just have to learn the basics once and for all and that is the main purpose of this post.
Besides this, running is the easiest form of physical exercise, you just need a pair of running shoes and then you can run anywhere at any time of the day.
I hope you get something out of this post and if you have any questions about the topic or want to leave your own Personal review, please leave a comment below.
[faq-schema id=”2881″]






Good post you have here and I can resonate well enough wuth this. The fact you have actually helped in simplifying all of these makes it even more better still. I really appreciate all you have shared and wow! It makes a lot of sense to me. Thank you so much for sharing this here with us. Thumbs up
Hi DarmiMaddie
Thank you for the comment. Happy that I could help wit some of it!
Be Well
I totally agree with you on this one. Not every activity, regarding the growth, health and wellness of the body, should be just about what we stand to benefit and gain health wise. We should also try to find the fun in these activities and even if there is none, we should try to make it fun. Thanks for writing this article to treat this topic and also enlighten us about the health benefits of running.
Hi Kevin
Thank you for the comment. Agree – and it’s also easier to maintain habits, we like doing.
Be Well
Woww, thank you for this very detailed information about the importance of running. I used to run 5 kilometers every evening after working for 12 hours when i was still single. And it felt so good! Even if i came tired from work, but “good feeling” that i feel afterwards was what pushed me to run despite being tired. Then after the short run, the tiredness was gone.
How i wish to go back running again. But right now i haven’t done any light exercises because i am still recovering from a repeat cesarean and scared that it will harm me than good.
Hi Julai
Thank you for the comment and your story. I can recognize that we can be tired after a long workday and still go for a run because of the “good feeling” afterwards. After your recovery it will be easier for you to start up again whenever you can / want, because you have already been there.
Be Well